Newsletter
Enter your e-mail to keep up to date on Melcalin® products
Newsletter
Enter your e-mail to keep up to date on Melcalin® products

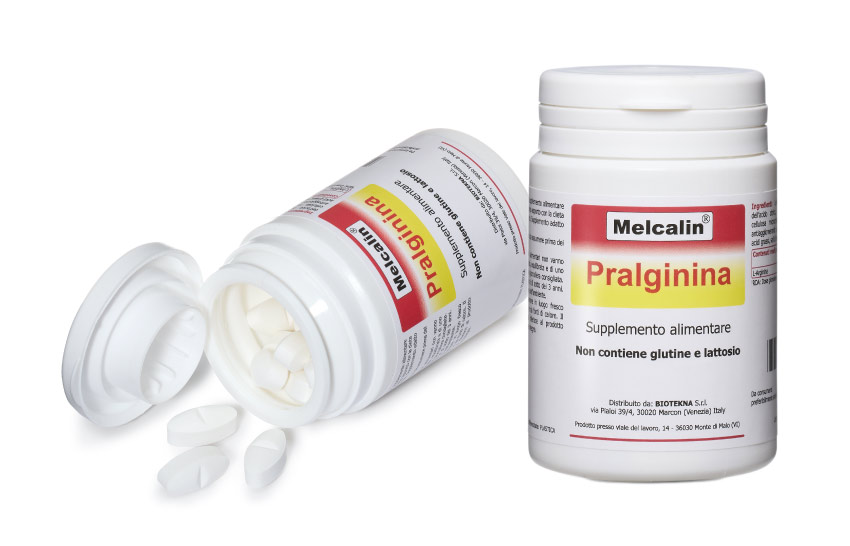
MELCALIN® IS A LINE OF FOOD SUPPLEMENTS SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE RECOVERY OF THE ACID-BASE BALANCE, OF THE METABOLIC AND NEUROIMMUNOENDOCRINE FUNCTIONALITIES, FOR THE RECOVERY OF VAGA AND ASPECIFIC SYMPTOMS (MUS) AND THE ACHIEVEMENT OF PSYCHOYS
PRODUCED BY BIOTEKNA © - BIOMEDICAL TECHNOLOGIES

MELCALIN® IS A LINE OF FOOD SUPPLEMENTS SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED FOR THE RECOVERY OF THE ACID-BASE BALANCE, OF THE METABOLIC AND NEUROIMMUNOENDOCRINE FUNCTIONALITIES, FOR THE RECOVERY OF VAGA AND ASPECIFIC SYMPTOMS (MUS) AND THE ACHIEVEMENT OF PSYCHOYS
PRODUCED BY BIOTEKNA © – BIOMEDICAL TECHNOLOGIES
Melcalin® is a registered trademark of BioTekna © | Biomedical Technologies | VAT number 01307750933