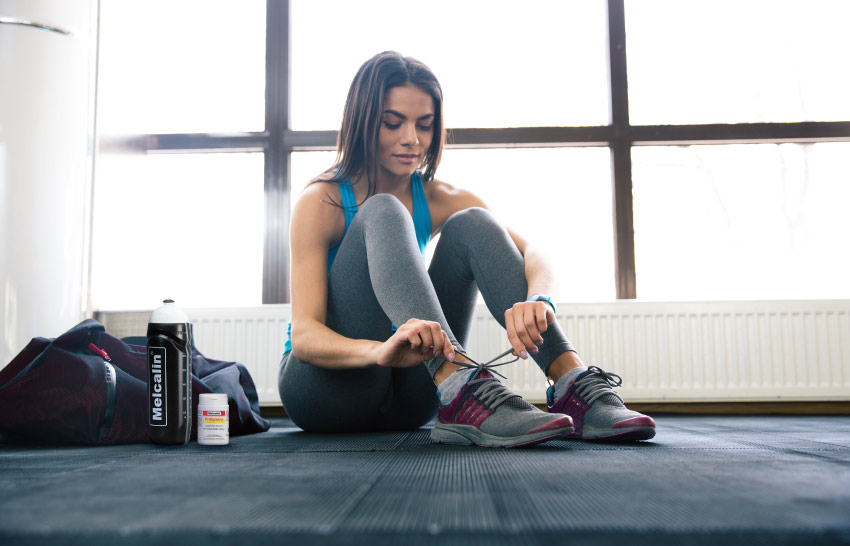
Introduction
Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid, essential for the production of nitric oxide 1,2.
Many of the activities of L-arginine, including its possible anti-atherogenic actions, can be explained by its role as a precursor of nitric oxide (NO), a molecule produced by all tissues of the body and capable of playing very roles. important in the cardiovascular system, the immune system and the nervous system 5.
Melcalin® Pralginina (PRAL negative L-arginine) is a food supplement containing buffered L-arginine; the formulation was designed with the addition of minerals such as potassium and magnesium since the acid-base balance is extremely important for the well-being of the whole body. Increases in the acidifying load are related to a number of problems such as the increase in systolic and diastolic pressure values, the increase in total cholesterol and LDL in addition to the reduction of the mineral content of bone tissue and loss of lean mass 26,27,28,29,30. Ensuring a correct pH for the body is therefore of fundamental importance for maintaining health in general25.
This association combines the multiple properties of L-arginine with the buffering action of the minerals that support its activity.
Arginine and Cardiovascular Risk (CVR)
The endothelium is a fundamental regulator of vascular homeostasis; its functionality can be altered by various factors such as smoking, hypertension, high cholesterol and diabetes mellitus7.
An important role in the regulation of the endothelial functionality is played by nitric oxide (NO), a substance released by the endothelium7 starting from L-arginine. Several studies have proven that the administration of L-arginine improves the endothelial function in subjects with high cholesterol and atherosclerosis, so much so that it has been hypothesized that it could be used as a possible treatment for coronary disease and peripheral artheriopathies3,5,6,7.
It has been proven that both the intake of arginine-rich food and long-term administration of L-arginine reduce cardiovascular complications and are inversely associated to endothelial dysfunction in high-cholesterol patientsbecause nitric oxide plays an important function in fat metabolism4.
L-arginine supplementation is able to decrease blood pressure and homocysteine levels: indeed, nitrogen oxide triggers a number of reactions that lead to the relaxation of smooth muscles and hence decreases blood pressure4.
Other researchers have highlighted that use of L-arginine leads to an increase in HDL and a decrease in cholesterol and triglycerides; specifically, a 7-day study on overweight men supplemented with L-arginine has shown a reduction of LDL and an increase in HDL3,4.
L-arginine plays a significant role in lowering glycemia: it has been proven that its use has improved glucose metabolism after 3-7 days of supplementation. It has been seen that L-arginine supplementation reduces glycemia in diabetic patients and scientific evidence shows that if taken for a prolonged period of time it can boost insulin sensitivity and improve glycemic indices; it seems that this results from its anti-oxidant activity3,4
Arginine and BAT (Brown Adipose Tissue)
The Brown Adipose Tissue (BAT) present in man plays an important role in the oxidation of fatty acids and glucose.
Several studies in the literature have proven that L-arginine can stimulate the development of BAT mitochondriaand induce gene expression regulation4.
L-arginine enhances the growth and development of BAT through mechanisms which involve gene expression and protein synthesis, which improves the oxidation of these energy substrates and hence reduces white fat buildups in the body: for this reason, L-arginine is believed to be very promising in the prevention and treatment of obesity in humans8.
Arginine and the Central Nervous System (CNS)
Nitric oxide (NO) is also an important regulator of the physiological processes in the central nervous system (SNC) in that it promotes optimal cerebral blood flow, consolidates memory processes, maintains the sleep-wake cycle and helps olfaction9.
Arginine and the Immune System
For several years, arginine has been used as a food supplement, often combined with other substances, as a mechanism to boost the immune system.
L-arginine plays an important role in regulating the immune system as it influences immune responses and inflammation. A piece of research has proven that subjects supplemented with L-arginine showed a lower incidence of infectious complications compared to the control group14.
As the production of nitric oxide (NO) starting from arginine is essential to defend the host from a number of pathogens, the availability of arginine is decisive for infection resistance; it has been seen that some pathogens are able to develop pathways that make it possible to degrade arginine in such a way as to avoid the immune system15.
Recent research has confirmed this, revealing that tumor cells express arginase (an arginine-degrading enzyme) and that this also occurs in cells after trauma or surgery16.
Arginine and Wounds
Arginine is classified as a non-essential amino acid that becomes a conditionally essential substrate in stressed adults.
Arginine is an amino acid that plays a number of different key roles in cell physiology. Like every amino acid, it is involved in the synthesis of proteins, but it is also intimately involved in cell signaling through the production of nitric oxide and cell proliferation. As a result of these multiple functions, arginine is an essential substrate for wound healing, so much so that some studies have highlighted that arginine increases wound resistance and collagen deposition in the area of injury and have proposed arginine supplementation to improve wound healing10,11.
Use of arginine can also be advised for diabetes as this condition impairs wound healing and as few therapeutic options are available to solve this issue. Data suggests that arginine supplementation improves the healing process by normalizing the production of nitric oxide, the latter being extremely important for wound scarring12,13.
Arginine and Sport
Arginine is a precursor of nitric oxide (NO); this molecule acts as signal to facilitate blood vessel dilatation and decrease vascular resistance. NO is synthesized by arginine, under the enzymatic control of nitric oxide synthase (NOS).
In the muscle, NO regulates the production of strength (excitation-contraction coupling), self-regulation of the blood flow, myocyte differentiation, breathing and glucose homeostasis. The contractile activity significantly increases the production of NO in the muscle, which, in turn, increases the release and absorption of fuel substrates through its vasodilating effects19.
Exercise performance has been analyzed after supplementation with L-arginine and physical performance has been found to be significantly improved by L-arginine as it promotes vasodilation and hence boosts the production of nitric oxide (NO) in the muscle and, as a result, improves strength, power and muscle recovery22.
Other research on sport performance (VO2 max) has shown that taking L-arginine results in an increase in muscular fatigue resistance and a significant increase in performance20.
It is well known that eccentric exercise interrupts sarcolemmal integrity and induces damage to skeletal muscle fibers; supplementation of L-arginine before eccentric exercise decreases the damage so induced23.
Satisfactory results have also been seen in post-menopausal women, in whom it has been found that the administration of L-arginine has increased maximum strength24.
The effects of oral supplementation of arginine on the ability to do exercise have been studied also in patients with pulmonary hypertension. A significant increase in the consumption of oxygen has been found and it has been hypothesized that arginine might possibly have a role in increasing nitric oxide, which translates into an increase in vasodilation and coronary vessels flow, which, in turn, can positively impact coronary perfusion21.
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction significantly limits the quality of life of a growing number of men. Given the increase in the conditions predisposing to the development of erectile dysfunction and given the aging of the male population, it is possible to mitigate the physical and psychological impact of erectile dysfunction by tackling risk factors through changes in the lifestyle combined with medical and surgical therapy in some patients.
Nitric oxide (NO) has been proven to relax the smooth muscles of the urogenital tract and is a well-known mediator of erection and of dilatation of the neck of the bladder and of the ureter. Oral high-dose L-arginine seems to determine a significant subjective improvement of the sexual function in men with this condition17,18.